Fads come and go. Many can be good, even if only briefly. A few might be bad enough to later stigmatize the object of the fad. For example, the formerly esteemed crape myrtle is now familiar as a mundanely common tree. Flashy bloom and complaisance contributed to its excessive popularity. Most sorts of juniper are similarly victims of their previous fad.
A few cultivars of juniper suddenly became overly popular during suburbanization of the 1950s. They were remarkably reliable and resilient. Most were shrubbery or low hedges. A few were groundcover. Hollywood juniper grew as a compact sculptural tree. However, most junipers grew too big. They became difficult to maintain, or impossible to renovate.
As many outgrew suburban gardens, few junipers outgrew their reputation. Even modern cultivars that were unavailable during the fad of the 1950s are perhaps less popular than they should be. Realistically, many old and new cultivars of juniper are quite practical for refined home gardens. They merely need to be appropriate to their particular application.
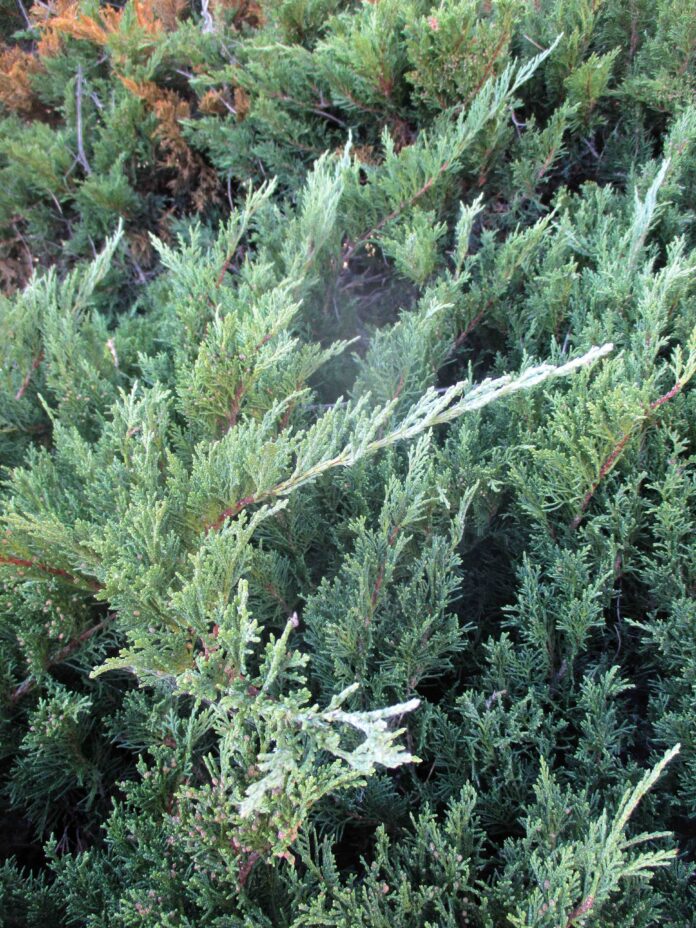
Many cultivars of several species of Juniperus are commonly available. Straight species are very rare from nurseries, although a few are native nearby. All junipers are evergreen with tiny awl or scale leaves. Foliar color ranges from forest green to silvery gray. Bloom is unremarkable. Some junipers produce pretty and aromatic blue, gray or black berries.
Junipers generally do not respond favorably to pruning that damages their natural forms. Those that grow as groundcovers, with stems that sprawl over the surface of the soil, are not offended by pruning to contain their edges. However, most groundcover junipers are actually just low shrubbery. Pruning might leave holes within their dense foliar canopies.
Junipers that grow as small trees do not mind removal of lower limbs at their main trunks, but object to partial pruning or “stubbing” of such limbs. Regardless of their natural forms, all junipers should be proportionate to their particular applications. With sufficient space, they can mature and develop their naturally distinguished forms with minimal altercation. Maintenance could really be quite minimal.
Highlight: Rocky Mountain juniper
Hollywood juniper had formerly been the only popular juniper of tree form. As it became less popular during the past few decades, cultivars of the once obscure Rocky Mountain juniper, Juniperus scopulorum, became more popular. Also, a few more modern cultivars became available. Now, the once overly common Hollywood juniper is quite uncommon.
Rocky Mountain juniper is naturally rather grayish for protection from the harsh exposure of the high elevations which it inhabits. Cultivars are grayer, bluish or silvery, and mostly develop symmetrically conical form. Old specimens that were initially conical eventually grow as small trees with rounded and relatively dense canopies, perhaps on bare trunks.
“Skyrocket” and “Blue Arrow” are very narrow like Italian cypress that grow only 15 feet tall. “Wichita Blue” and “Moonglow” are stoutly conical. “Blue Arrow” and “Wichita Blue” are bluish green. “Skyrocket” and “Moonglow” are silvery gray. Established specimens do not require much water, but develop better foliar color with warmth and occasional watering.
Tony Tomeo can be contacted at tonytomeo.com.