Within the outdoor rooms of home gardens, shade trees are ceilings, shrubs and hedges are walls, and turf and ground cover plants are floors. That is why the selection of plants for such purposes is as important as the selection of paint and carpet for indoors. Among ground cover plants, durable turf grasses for lawns are the most common and functional.
There are so many more types of ground cover plants besides turf grasses though. A few of the lower, denser and more resilient types of ground cover plants can function as turf if necessary. Many more function as mulch to control erosion, contain dust or conceal mud. Many inhibit proliferation of weeds. Some retain a bit more moisture than they consume.
Appropriate ground cover plants most definitely have many advantages. They also have certain disadvantages. Although most require less maintenance than the weeds that they exclude, they require more maintenance than simple mulch. Also, most require irrigation. They might be trailing perennials, sprawling shrubbery, or unsupported wandering vines.
Trailing gazania, Hottentot fig (freeway “ice plant”) and various ice plants are some of the more popular perennial ground cover plants. They and others migrate by trailing stolons or rhizomes. They are among the lower and more compact types of ground cover plants. Some need no more pruning than edging. Many propagate easily by division or cuttings.
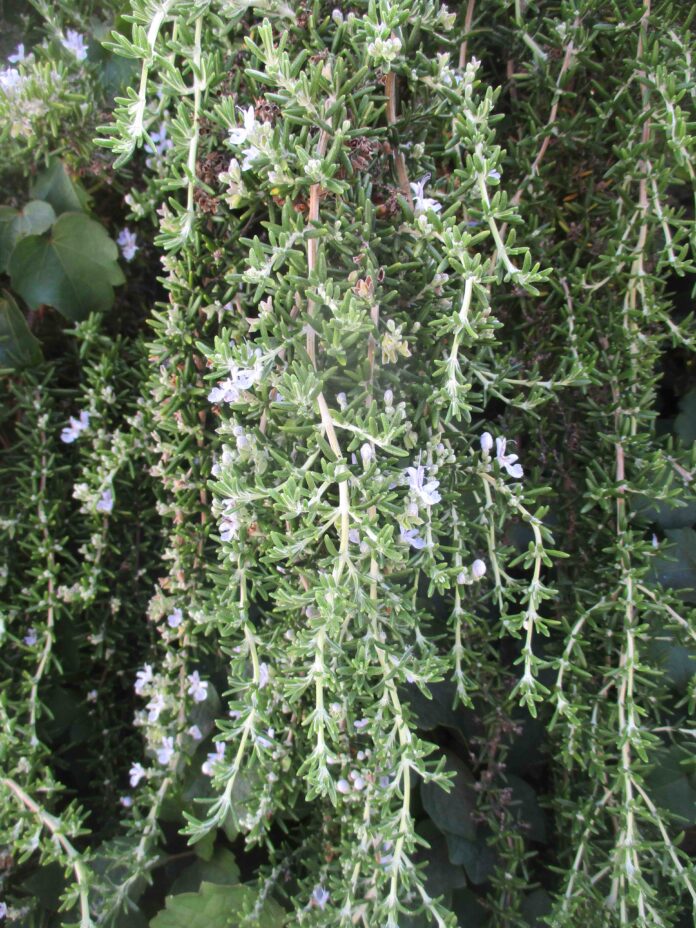
Sprawling sorts of juniper, ceanothus, cotoneaster, myoporum and rosemary are shrubby ground cover plants. They get significantly deeper than perennial plants, and some sorts can eventually get too overgrown to be practical. Rosemary, myoporum and cotoneaster are conducive to shearing as they mature. Ceanothus and juniper need significant area.
English ivy, Algerian ivy and star jasmine are vining ground cover plants that should stay rather low if properly maintained. However, they can climb into shrubbery and trees, and even buildings. The ivies are famously aggressive, and spread indefinitely by rooting as they migrate. Severe pruning can renovate some overgrown vining ground cover plants. Bougainville gets rather shrubby and deep, even without support.
Highlight: Irish moss
It is not actually moss. It is of the same family as carnation. Of course, any distinguishing characteristics of its family are difficult to recognize. Iris moss, Sagina subulata, has such exceptionally fine foliar texture and diminutive bloom. Its slim leaves are not much longer than a quarter of an inch. Its tiny white flowers are barely wider than an eighth of an inch.
Irish moss is a luxuriantly dense and richly evergreen ground cover for confined spaces. It works well within small atriums and big pots that contain sculptural plants that lack low foliage. It is a popular accessory for Japanese maple and citrus within tubs. Since it gets no more than two inches deep, Irish moss can fill in between pavers and under benches.
However, Irish moss dislikes how pavement enhances harsh exposure. Although it does not require shade, it appreciates a bit of partial shade while the weather is warmest after noon. Also, it craves somewhat frequent watering to compensate for locally arid warmth. Scottish moss is the cultivar “Aurea.” It is lighter chartreuse green, but otherwise identical.
Tony Tomeo can be contacted at tonytomeo.com.